
Topkappy is a Python library for using the Kappa biological modeling system.
It is built on top of kappy, the official Python binding for Kappa, and
provides a more pythonic interface to define models and analyse results:
Python objects to define agents and rules, methods for visualizing complexes and
plotting time series, pretty error printing, etc.
Example¶
Here is a standard Kappa script defining a situation with 3 agents A, B, C which can irreversibly bind together to form A-B-C chains. We end the simulation after 10 (virtual) seconds and take a snapshot.
%agent: A(a, b)
%agent: B(b, c)
%agent: C(c, d)
'a.b' A(b[.]),B(b[.]) -> A(b[1]),B(b[1]) @ 0.005
'b.c' B(c[.]),C(c[.]) -> B(c[1]),C(c[1]) @ 0.021
%init: 100 A()
%init: 100 B()
%init: 100 C()
%mod: alarm 10.000 do $SNAPSHOT "end";
%plot: |B(b[.])|
%plot: |C(c[.])|
Now here is the same model defined in Python with Topkappy:
from topkappy import KappaModel, KappaAgent, KappaRule, KappaSiteState)
model = KappaModel(
agents = [
KappaAgent('A', ('a', 'b')),
KappaAgent('B', ('b', 'c')),
KappaAgent('C', ('c', 'd'))
],
rules = [
KappaRule(
'a.b',
[
KappaSiteState('A', 'b', '.'),
KappaSiteState('B', 'b', '.')
],
'->',
[
KappaSiteState('A', 'b', '1'),
KappaSiteState('B', 'b', '1')
],
rate=0.5e-2
),
KappaRule(
'b.c',
[
KappaSiteState('B', 'c', '.'),
KappaSiteState('C', 'c', '.')
],
'->',
[
KappaSiteState('B', 'c', '1'),
KappaSiteState('C', 'c', '1')
],
rate=2.1e-2
)
],
initial_quantities={
'A': 100,
'B': 100,
'C': 100,
},
duration=10,
snapshot_times={
'end': 10
},
plots=[KappaSiteState('B', 'b', '.'),
KappaSiteState('C', 'c', '.')]
)
# Now simulate the model !
simulation_results = model.get_simulation_results()
The Python version is admittedly longer than the original Kappa script, but where Python shines is in its ability to programmatically define much more complex and dynamic models with dozens of agents and rules.
Topkappy also makes it easy to simulate the result and get the final data, and provide a few utilities to vizualize the results. For instance let us plot the two time series records during the simulation:
from topkappy import plot_simulation_time_series
ax = plot_simulation_time_series(simulation_results['plots'])
ax.figure.savefig('basic_example_time_series.png')
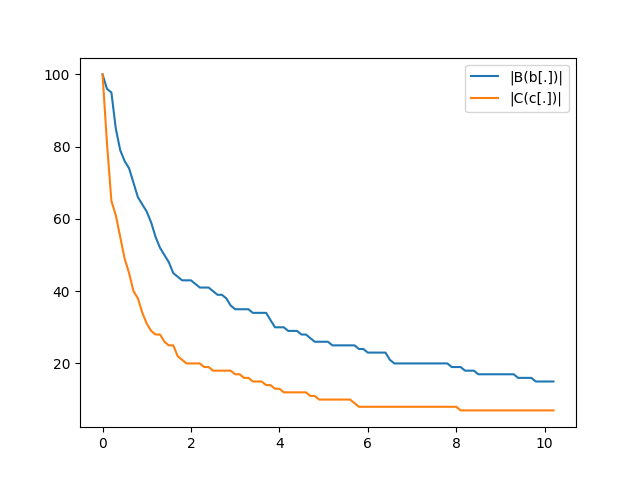
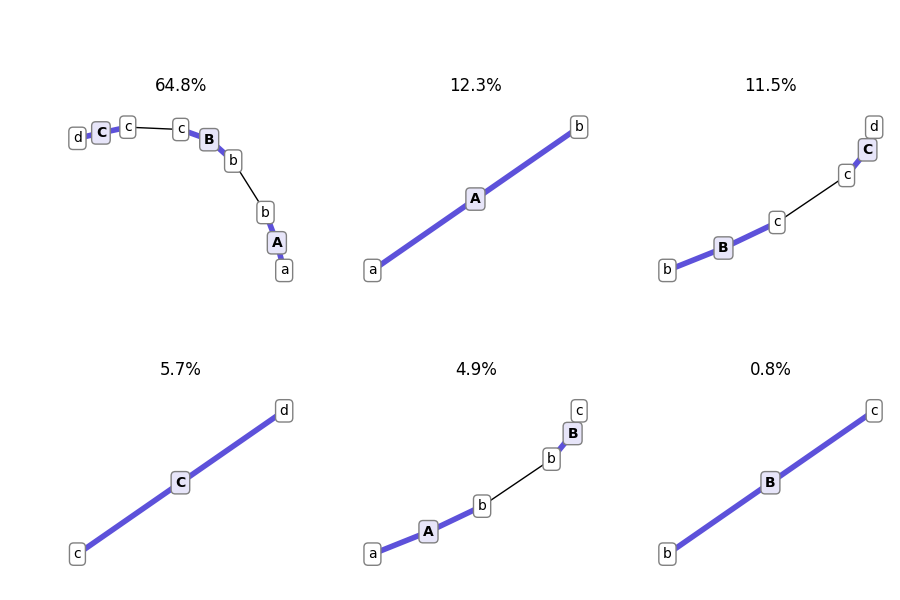
And here is how you plot the products present at the end of the simulation:
end_agents = simulation_results['snapshots']['end']['snapshot_agents']
fig, axes = plot_snapshot_agents(end_agents)
fig.savefig('basic_example_agents_graphs.png')
Installation¶
You can install topkappy through PIP:
sudo pip install topkappy
Alternatively, you can unzip the sources in a folder and type:
sudo python setup.py install
License = MIT¶
Topkappy is an open-source software originally written at the Edinburgh Genome Foundry by Zulko and released on Github under the MIT licence (Copyright 2018 Edinburgh Genome Foundry).
Everyone is welcome to contribute!
More biology software¶

Topkappy is part of the EGF Codons synthetic biology software suite for DNA design, manufacturing and validation.